


(ii) For exothermic process may be non spontaneous at high temp. (i) For endothermic process may be non spontaneous at law temp. Effects of T on spontaneity of a process : ∆G = W (useful) = W (max).If G = ve, process is spontaneous.
#SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS PDF FREE#
Gibb’s free energy (G) :ĭefined as G = H – T.S & ∆G = ∆H – T.∆S (Gibb’s Helmholts equation) it is equal useful work. A spontaneous process cannot be reversed.
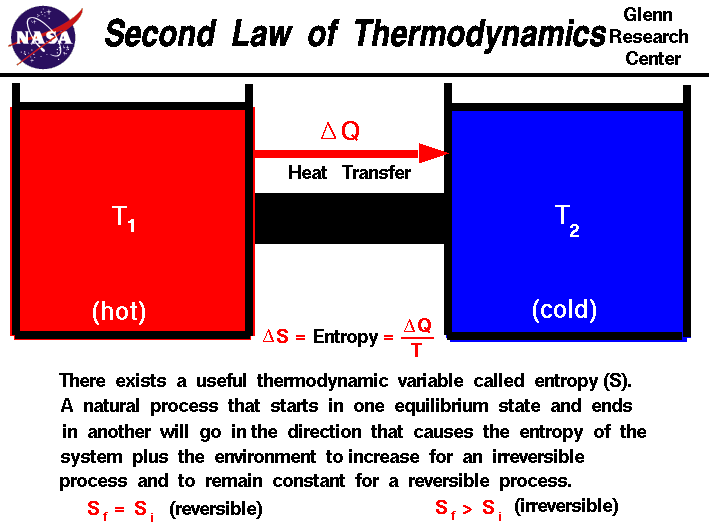
In any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe always increases. ∆S (total) = ∆S (universe) = ∆S (system) + ∆S (surrounding) If ∆S (total) is +ve, the process is spontaneous If ∆S (total) is –ve, the process is non spontaneous. It is measure of randomness or disorder of system.i.e. A process which can neither take place by itself or by initiation is called non Spontaneous. (Products) Spontaneous & Non Spontaneous Processes :Ī process which can take place by itself is called spontaneous process. It is amount of energy released when gaseous atoms combines to form one mole of bonds between them or heat absorbed when one mole of bonds between them are broken to give free gaseous atoms. ( i ) Enthalpy of combustion (∆ cH) ( ii) Enthalpy of formation (∆ fH) Different types of Enthalpies of reactions:

Standard Enthalpy of reaction ( ∆ rH o) at 1 bar pressure and specific temp. The amount of heat evolved or absorbed when the reaction is completed. evolution and absorption of heat.ĬO 2 + 393.5 KJ, H = –393.5 KJ (exothermic)ĢNO – 180.7 KJ, H = 180.7 KJ (Endothermic) Enthalpy of reaction ( ∆ rH) : ∆H = –Ve for exothermic and ∆H = +Ve for endothermic reaction i.e. ∆H& ∆U It is ∆ H= ∆U+ ∆ng.RT or q p = q v + ∆ ng.RT Exothermic and Endothermic reactions : ∆V, q,w are not state function. ∆But U is state function.Īt constant volume ∆V = 0,qv =∆So H = U + p. V∆ (work of expansion) ∆U = q – p. ∆ V or q = ∆ U + p. Energy can neither be created not destroyed, it may be converted from one from into another. Mathematically ∆U = q + w, w = –p. Unit is Joule (J) or Calorie (1 Calorie = 4.18 J). It I a form of energy which is exchanged between system and surrounding due to difference of temperature. i.e. U = E e E n + E c + E p + E k + - ∆ U = U 2 – U 1 or U P – U R & U is state function and extensive properly. T,P, density, refractive index, viscosity, bp, pH, mole fraction etc. The properties which do not depends on matter present depends upon nature of substance called Intensive properties. mass, volume, heat capacity, enthalpy, entropy etc. Properties which depends on quantity of matter called extensive prop. The property which depends only on state of system not upon path is called state function eg. State of system is described in terms of T, P, V etc. The part of universe for study is called system and remaining portion is surroundings. Science which deals with study of different forms of energy and quantitative relationship. Zeroth Law Second Law 3rd Law Thermodynamics :


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
